Glucagon treatment for hypoglycaemia
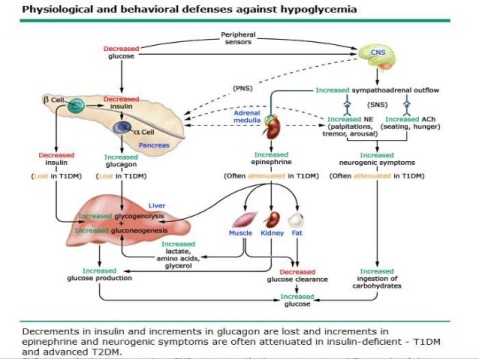
Unless corrected, hypoglycemia will lead to unconsciousness, convulsions (seizures), and possibly death.
Early symptoms of hypoglycemia include: anxious feeling, behavior change similar to being drunk, blurred vision, cold sweats, confusion, cool pale skin, difficulty in concentrating, drowsiness, excessive hunger, fast heartbeat, headache, nausea, nervousness, nightmares, restless sleep, shakiness, slurred speech, and unusual tiredness or weakness.
You should know what to do if symptoms of low blood sugar occur. Eating or drinking something containing sugar when symptoms of low blood sugar first appear will usually prevent them from getting worse, and will probably make the use of glucagon unnecessary. Good sources of sugar include glucose tablets or gel, corn syrup, honey, sugar cubes or table sugar (dissolved in water), fruit juice, or nondiet soft drinks. If a meal is not scheduled soon (1 hour or less), you should also eat a light snack, such as crackers and cheese or half a sandwich or drink a glass of milk to keep your blood sugar from going down again. You should not eat hard candy or mints because the sugar will not get into your blood stream quickly enough. You also should not eat foods high in fat such as chocolate because the fat slows down the sugar entering the blood stream. After 10 to 20 minutes, check your blood sugar again to make sure it is not still too low.
Glucagon administration
If severe symptoms such as convulsions (seizures) or unconsciousness occur, the patient with diabetes should not be given anything to eat or drink. There is a chance that he or she could choke from not swallowing correctly. Glucagon should be administered and the patient’s doctor should be called at once.
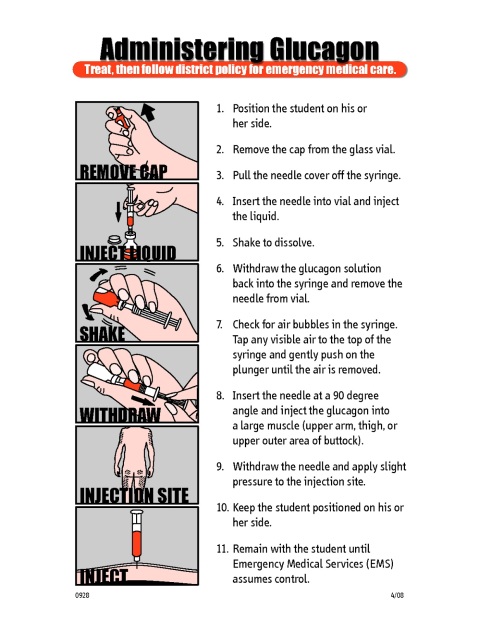
If it becomes necessary to inject glucagon, a family member or friend should know the following:
After the injection, turn the patient on his or her left side. Glucagon may cause some patients to vomit and this position will reduce the possibility of choking.
The patient should become conscious in less than 15 minutes after glucagon is injected, but if not, a second dose may be given. Get the patient to a doctor or to hospital emergency care as soon as possible because being unconscious too long can be harmful.
Replenish the body’s glucose supply
When the patient is conscious and can swallow, give him or her some form of sugar. Glucagon is not effective for much longer than 1½ hours and is used only until the patient is able to swallow. Fruit juice, corn syrup, honey, and sugar cubes or table sugar (dissolved in water) all work quickly. Then, if a snack or meal is not scheduled for an hour or more, the patient should also eat some crackers and cheese or half a sandwich, or drink a glass of milk. This will prevent hypoglycemia from occurring again before the next meal or snack.
Monitor
The patient or caregiver should continue to monitor the patient’s blood sugar. For about 3 to 4 hours after the patient regains consciousness, the blood sugar should be checked every hour.
If nausea and vomiting prevent the patient from swallowing some form of sugar for an hour after glucagon is given, medical help should be obtained.
source
http://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/glucagon-injection-route/precautions/drg-20064089
